As generative AI evolves and opens new opportunities for business growth, productivity, and innovation, it also introduces new security challenges. Hence, GenAI adoption should be safe, responsible, and resilient. Organizations must now focus on AI-specific security strategies to address emerging threats like exposure to sensitive data, model manipulation, and adversarial attacks.
To ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and resilience of GenAI systems, AWS provides best practices, frameworks, and tools designed to secure every layer, from infrastructure to inference. In this blog, we will cover the unique security challenges, AWS’s proven methodologies for defense, and practical guidance for safeguarding generative AI workloads.
Considerations for AI Security
As threats to generative AI workloads continue to evolve, organizations should take a proactive approach to assessing and managing risks throughout their entire lifecycle. To truly protect these generative AI workloads on AWS, implement a multi-layered approach that covers the application, platform, network, and data layers. Establish clear boundaries and enforce strict access controls by applying the principle of least privilege across all components. For secure communication, use private networks and implement monitoring and guardrails to detect and respond to threats. System design should include structured threat modeling frameworks such as MITRE ATLAS and OWASP Top 10 for LLMs to identify and prioritize potential vulnerabilities.
Layered Approach to AI Defense in AWS
Layer 1: Infrastructure & Network Security
The foundation for securing GenAI workloads on AWS begins with protecting the underlying infrastructure, which encompasses network, compute, and identity elements. To achieve this, place the generative AI workloads in dedicated Amazon VPCs within private subnets, with network isolation defined through security groups and NACLs. For secure and internet-free communication between VPCs and AWS services, leverage Amazon VPC endpoints and AWS PrivateLink.
For compute security on AWS, use Nitro-based instances that provide hardware-level isolation by design, and ensure Amazon EC2 instances running AI workloads remain secure through regular hardening and automated patching. SageMaker's built-in security capabilities can also be used to secure machine learning workflows and data. Containerized workloads should be secured with Amazon Inspector, which continually scans Amazon Elastic Container Registry (ECR) for software vulnerabilities and unintended network exposures.
For access control, enforce least-privilege AWS IAM roles scoped specifically for AI services in use. Implement multi-account isolation using AWS Organizations to maintain separate and secure environments. Record and monitor all identity-related activities using AWS CloudTrail’s detailed audit logs. To keep AI infrastructure secure against emerging threats, implement continuous threat detection with Amazon GuardDuty and regularly validate compliance using AWS Config.
Layer 2: Model Security
To effectively secure AI models, protection is required throughout their lifecycle, from development to deployment. During data collection, model artifacts stored in Amazon S3 and Amazon SageMaker model registries can be protected at rest using encryption with AWS KMS. To safeguard model inference endpoints, use private Amazon VPC configurations and token-based authentication to block unauthorized access.
Building strong model governance is crucial to keeping AI models secure. Use Amazon SageMaker Model Registry for version control and to track model history. Set up approval workflows to avoid any unauthorized changes. For custom models, use Amazon SageMaker's model monitoring capabilities to detect concept drift and potential adversarial inputs. Implement custom metrics to identify abnormal inference patterns that could indicate exploitation attempts. Deploy Amazon Bedrock guardrails to filter harmful content and implement input validation layers to defend against prompt injection attacks that could manipulate model behavior.
These technical controls should be complemented with standard model security assessments and testing for vulnerabilities like prompt leakage. Implement strict access controls for model weights and hyperparameters to prevent intellectual property theft or model extraction attacks.
Layer 3: Data Security
Data security is essential for every organization, and a comprehensive data security approach should be followed across the entire business. Implement end-to-end encryption using AWS KMS with customer-managed keys for data at rest in Amazon S3, Amazon EBS volumes, and Amazon SageMaker notebooks. Secure data in transit with TLS. To restrict access to the training dataset for authorized users and services, use Amazon S3 bucket policies, AWS IAM roles, and attribute-based access control (ABAC) to implement fine-grained access control (FGAC).
Amazon S3 Object Lambda can be used to anonymize, tokenize, or redact sensitive data before it reaches the AI model. Use AWS Macie for automated discovery and classification of sensitive information. Ensure data governance with AWS Glue Data Catalog for lineage tracking and AWS Lake Formation for central permission management. Apply differential privacy to minimize the exposure of sensitive data during training. Generate synthetic data using Amazon SageMaker Feature Store to make it difficult for attackers to reverse-engineer individual data points. Prevent data exfiltration by configuring Amazon VPC endpoints with restrictive policies. Use Amazon S3 Access Points with dedicated permissions to limit access to sensitive data. Monitor data access patterns with AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch to detect anomalies.
Conduct regular security assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure ongoing protection. Implement strict data minimization practices to reduce risk. Automate lifecycle policies to manage the retention and secure deletion of AI datasets when they are no longer required. To protect models from poisoning during pre-training and ongoing training, isolate the model training environment, infrastructure, and associated data. Additionally, all data should be thoroughly examined and cleaned for potentially harmful content before being used for training purposes.
Layer 4: Application/Inference Security
The application layer of generative AI workloads must be safeguarded. To ensure this, use AWS WAF with custom rule sets to detect AI-specific threats like prompt injection attempts. Enable rate limiting and geographic restrictions to prevent abuse, and deploy AWS Shield Advanced for high-risk deployments. Create application-specific Amazon CloudWatch dashboards to visualize unusual usage patterns.
Amazon API Gateway can be configured with request validation and throttling to provide a controlled interface to AI models. Implement AWS Lambda functions to preprocess inputs, sanitizing and validating them before they reach the models. Applications can be secured with AWS Cognito for authentication and session management.
Use Amazon Bedrock guardrails or custom content filtering solutions to enforce appropriate use policies and prevent harmful outputs. Leverage Amazon Comprehend for toxic content detection and apply jailbreak detection to identify boundary violations. Monitor inference patterns with Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor to detect adversarial inputs that could manipulate model behavior.
Establish continuous security testing practices, including prompt injection penetration testing and regular code reviews using AWS CodeGuru, to ensure ongoing security. These steps help uncover vulnerabilities in the application logic and keep generative AI applications resilient against evolving threats.
Layer 5: Runtime Security
Real-time threat detection is essential for securing AI workloads. Use Amazon GuardDuty’s machine learning capabilities to identify suspicious activities, and leverage AWS CloudTrail and Amazon CloudWatch for API monitoring and anomaly detection. Amazon Inspector can perform vulnerability scans on compute resources and support Amazon ECR image scanning. For containerized AI workloads, implement AWS App Mesh to establish zero-trust networking between services.
Deploy Amazon SageMaker Model Monitor to detect concept drift, data issues, and unusual inference patterns that might indicate exploitation. Resource-based guardrails can be established using AWS Service Quotas and custom throttling to prevent resource exhaustion attacks and reduce costly inference misuse. Create automated response workflows with Amazon EventBridge and AWS Lambda functions. This enables remediation actions, such as isolating compromised resources or scaling defenses during active attacks when security anomalies are detected.
Implement real-time prompt and output analysis using custom Lambda functions to identify and block potential jailbreak attempts or sensitive data leakage during inference. Comprehensive audit logs can be maintained with Amazon CloudWatch Logs Insights to support security investigations. Use AWS Config for continuous compliance monitoring and AWS Systems Manager to support secure operational management of AI resources. Together, these measures secure generative AI workloads throughout their lifecycle.
Practical Example: Mitigation Strategy for Prompt Injection in QnA Chatbot
In this scenario, an e-commerce company deploys a generative AI-powered chatbot to assist both B2B users and customer support representatives. The chatbot handles tasks such as checking product inventory, obtaining real-time pricing, and placing orders without human intervention. This automation streamlines operations and reduces routine call volumes while exposing prompt injection risks. Malicious users could craft input designed to manipulate the chatbot's responses. Such manipulations could bypass security filters or access unauthorized information. This might lead to data breaches or unintended actions that compromise the integrity and safety of the AI-driven support system.
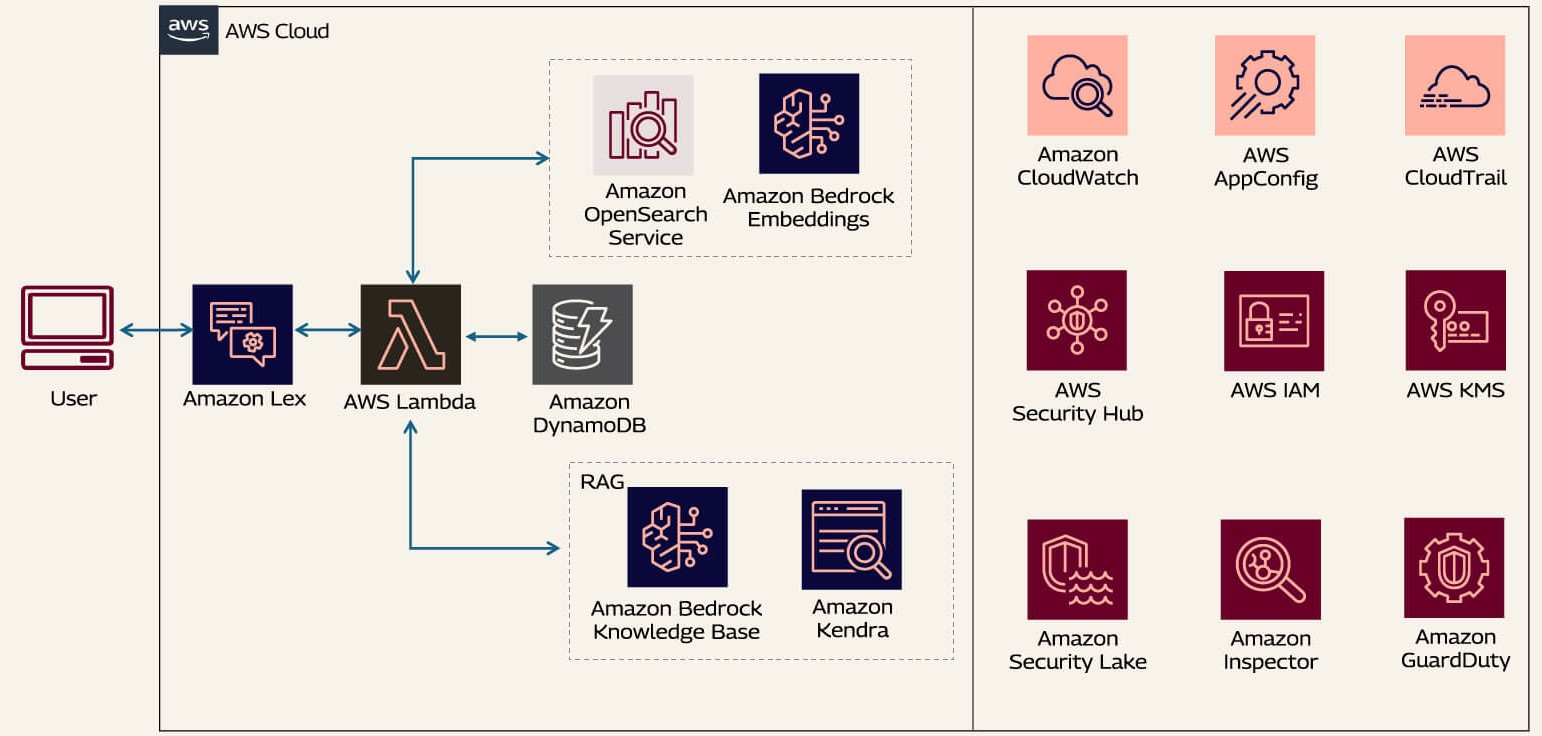
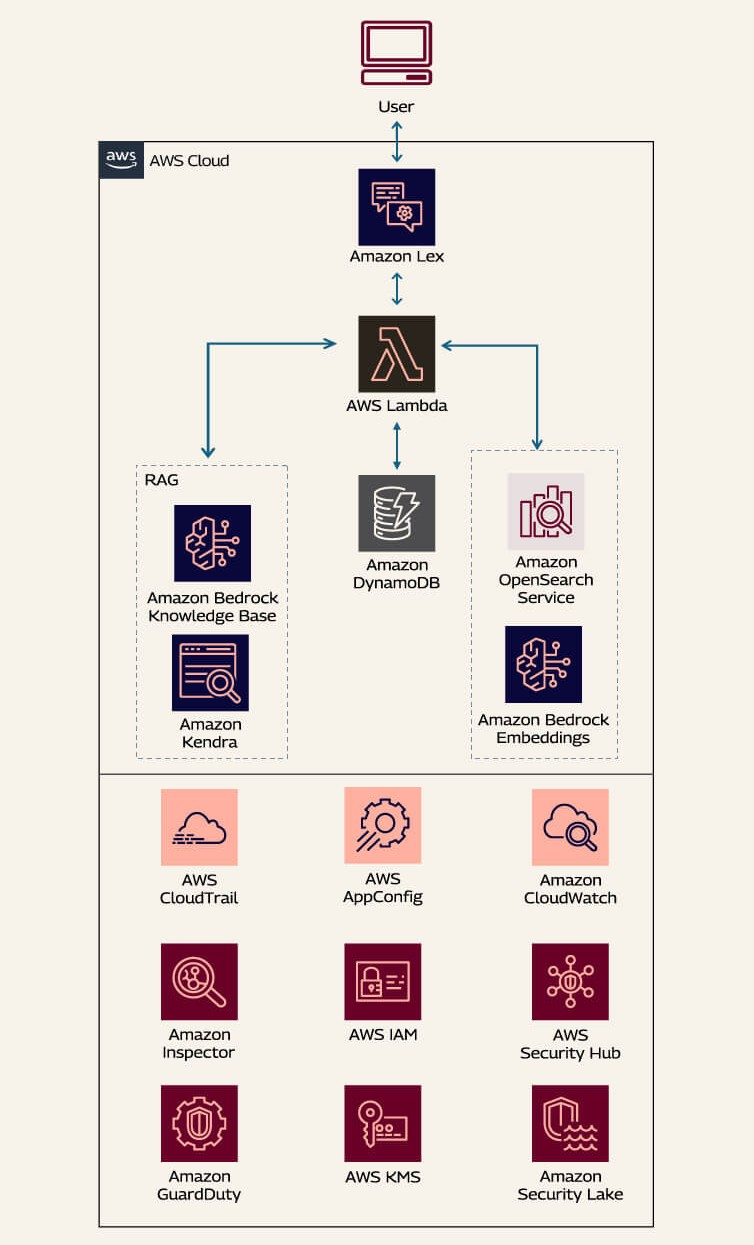
To protect AI models against prompt injection attacks, a proactive approach is essential. This involves combining multiple strategies to create a robust defense mechanism. Here are some key steps to consider:
1. Input Validation and Sanitization
Input validation and sanitization are essential to protect AI models from prompt injection attacks. A threat actor could inject malicious code, such as SQL code, leading to unauthorized access or manipulation of the DynamoDB chat history data.
Effective input validation is necessary to make sure data entering the system is safe. This includes filtering out potentially harmful prompts by removing or escaping special characters and control sequences, as well as limiting input length to prevent complex injection attempts.
Validate user input with AWS Lambda and Amazon API Gateway before sending them to LLMs (Large Language Models) for processing. Use Amazon Macie for data classification. For a generative AI system, configure AWS Web Application Firewall (WAF) rules to inspect incoming requests. AWS WAF will filter out suspicious patterns such as excessively long inputs, known malicious strings, or attempts at SQL injection.
2. Content Moderation
Content moderation can be implemented at various stages of an application’s process. Monitoring user-generated content and AI-generated responses reduces the risk of code injection or exposure to harmful material.
Amazon Bedrock Guardrails allows you to set up filters for prohibited topics and content. These filters can automatically remove sensitive data such as personally identifiable information (PII). They also detect and block other harmful content from user interactions within the application.
It is advisable to implement several layers of input validation for critical actions. Input guardrails act as the system’s first line of defense by screening and blocking potentially harmful queries before they reach the language model. This prevents inappropriate or malicious user inputs from entering the QnA Bot workflow.
Within Bedrock, guardrails can be applied at the inference stage. These guardrails work for both LLMs and knowledge bases to provide context-aware filtering and safety checks. This ensures that accurate and appropriate answers are generated.
Similarly, output guardrails serve as a final checkpoint. They review model responses before delivering them to users by scanning, masking, or blocking sensitive and inappropriate content in the AI’s replies. This helps in safeguarding against accidental exposure of PII or other restricted material before any information is returned through the fulfillment Lambda.
This comprehensive approach ensures both user input and model outputs are thoroughly vetted for safety and compliance. To protect against jailbreak attempts and prompt injections that could manipulate the model into generating harmful or unintended content, use Amazon Bedrock Guardrails’ “prompt attack” filter.
3. Security and Testing
Adopt secure coding standards by utilizing parameterized queries and avoiding string concatenation for user input. Apply the principle of least privilege when assigning resource permissions. Make this a routine to test your applications for vulnerabilities like prompt injections through methods like penetration testing, static analysis, and dynamic application security testing (DAST). Ensure that your Amazon Bedrock SDK, libraries, and other dependencies remain up to date with the latest security releases. Monitor AWS security advisories to stay informed about new patches and recommendations.
4. Monitoring and Response
Monitoring and response involve several steps, including monitoring model inputs and outputs to detect unusual patterns, implementing logging systems to track potential attacks, and creating feedback loops to improve security defenses continuously.
AWS offers several services to support these efforts. You can use AWS CloudTrail and AWS CloudWatch to log and monitor your generative AI applications. Enable tracing in Amazon Bedrock Guardrails and monitor performance with CloudWatch metrics. Together, these tools help you detect issues early and respond effectively.
Use Amazon Comprehend for natural language processing to detect potentially harmful content.
5. User Authentication
To ensure proper security, implement user authentication for sensitive operations. Apply different trust levels based on user verification, and limit capabilities for unauthenticated users. Use Amazon Cognito, which provides robust authentication and authorization mechanisms for frontend users.
Organizations should apply zero-trust security principles and least privilege access when managing AI workloads on AWS. This includes using IAM roles with tightly defined permissions and setting permission boundaries. Separate duties among different roles for developers and security engineers, and configure service roles for Bedrock agents and prompt flows. These measures will limit unnecessary access and strengthen security at both the account and organizational levels.
Conclusion
To build powerful and secure AI systems, organizations must implement strong controls at the infrastructure, data, model, and inference layers. A comprehensive approach that encompasses data protection, access control, continuous monitoring, incident response, and compliance will serve as a strong backbone for securing AI workloads on AWS.
AWS offers a host of services and features that enable organizations to implement AI security by design. Adopting the best practices discussed in this blog and leveraging AWS's security capabilities will help you achieve confidence in deploying AI systems that protect sensitive data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain the integrity of your AI operations.