Nowadays, every customer, associate, and company is discussing AI capabilities, which include GenAI. Moreover, most customers expect GenAI solutions to address various use cases in software development, testing, test automation, application maintenance, and support. But are they one and the same? If not, how are they different, and how do we know which one to use in a specific scenario? Let’s break it down.
GenAI vs Agentic AI
GenAI leverages Large and Small Language Models (LLMs/SLMs) to respond to user queries and generate outputs. These outputs typically go through a review and enhancement cycle to ensure they are ready for use. The next step in this evolution is Agentic AI, where the AI system can autonomously perform tasks based on predefined objectives, moving from simple output generation to autonomous task execution.
| Feature | Agentic AI | Generative AI |
|---|---|---|
| Inputs Required | Agentic AI requires a set of AI agents, each responsible for a particular task. | Generative AI operates based on user prompts, supported by context and examples. |
| Feedback Loop | Incorporates a continuous feedback loop that enables the self-improvement of agents. | Relies on manual feedback to refine outputs and improve accuracy. |
| Role in SDLC | Manages and orchestrates tasks to achieve end-to-end goals across the SDLC. | Generates code, test cases, and documentation to support development activities. |
How Agentic AI Works
Unlike traditional GenAI tools that respond to a single prompt, Agentic AI systems operate through a multi-agent workflow, where each agent is assigned a specific task and works toward a shared objective.
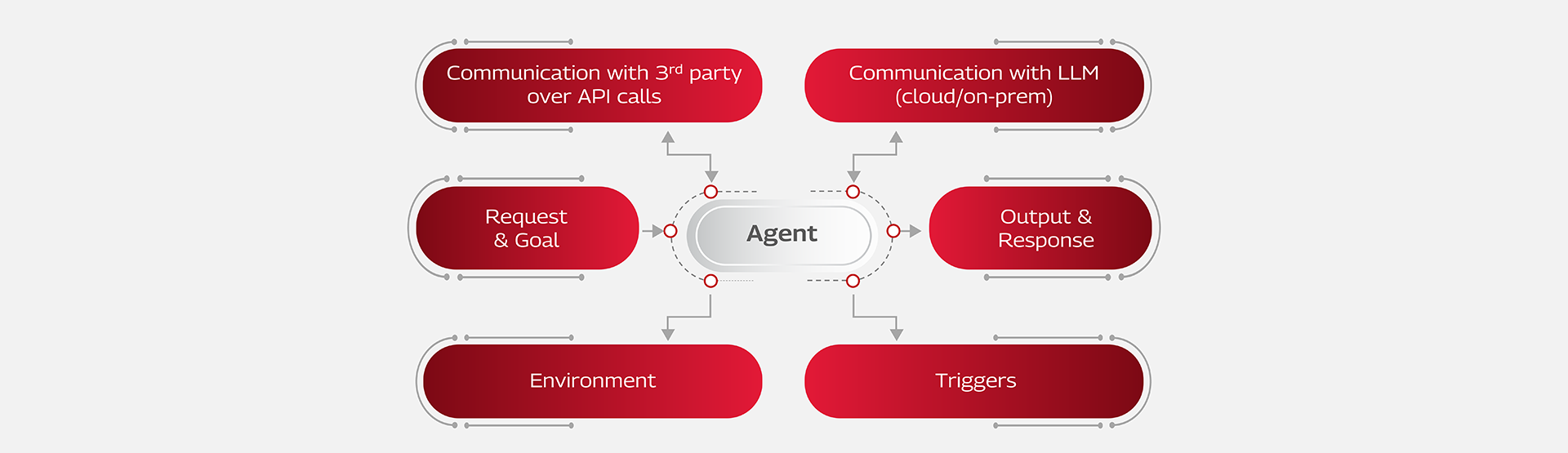
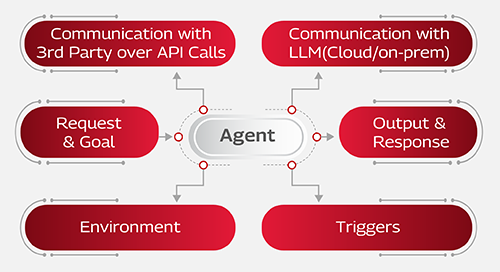
Agentic AI represents a structured workflow composed of a set of AI agents or bots, each designed to perform a specific task in pursuit of a defined goal based on the order of agents. Each AI agent or bot acts as a subcomponent within the Agentic AI use case, performing a specific task.
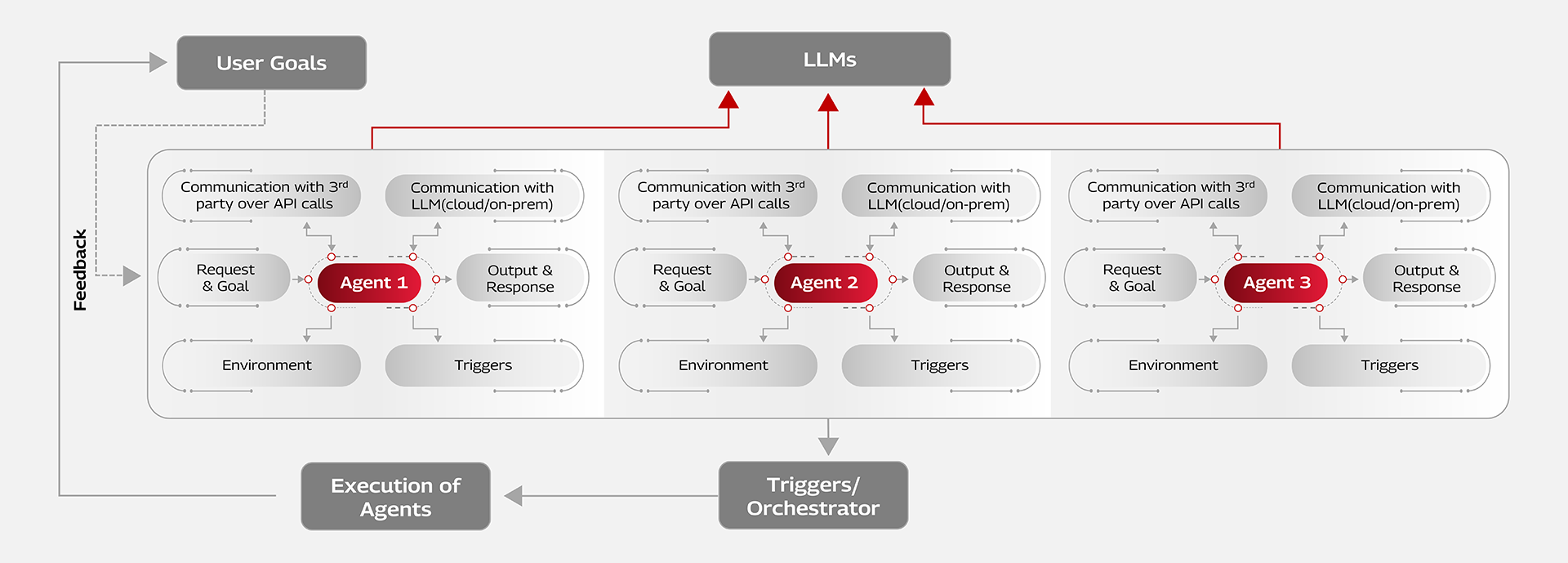
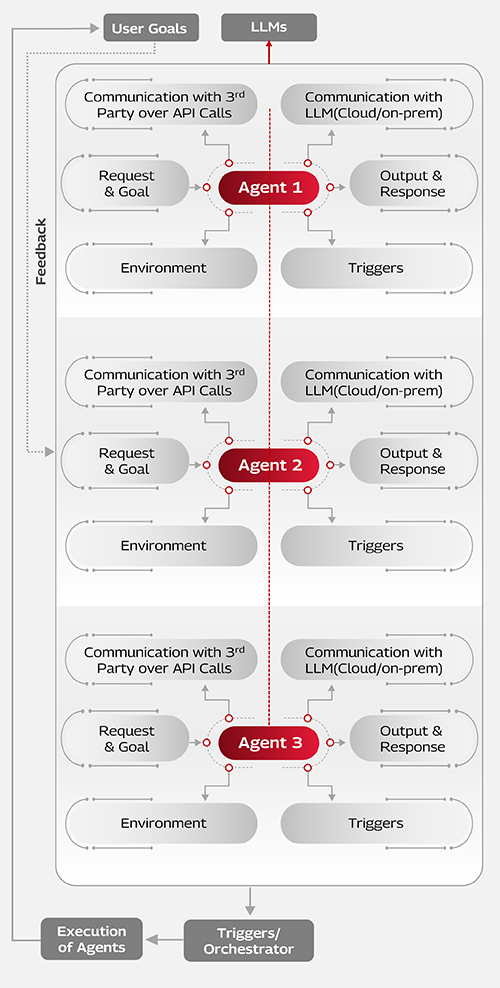
Implementing Agentic AI use cases requires a focused and structured approach supported by the right frameworks, tools, environments, and clearly defined goals. These components are essential for developing effective and scalable use cases.
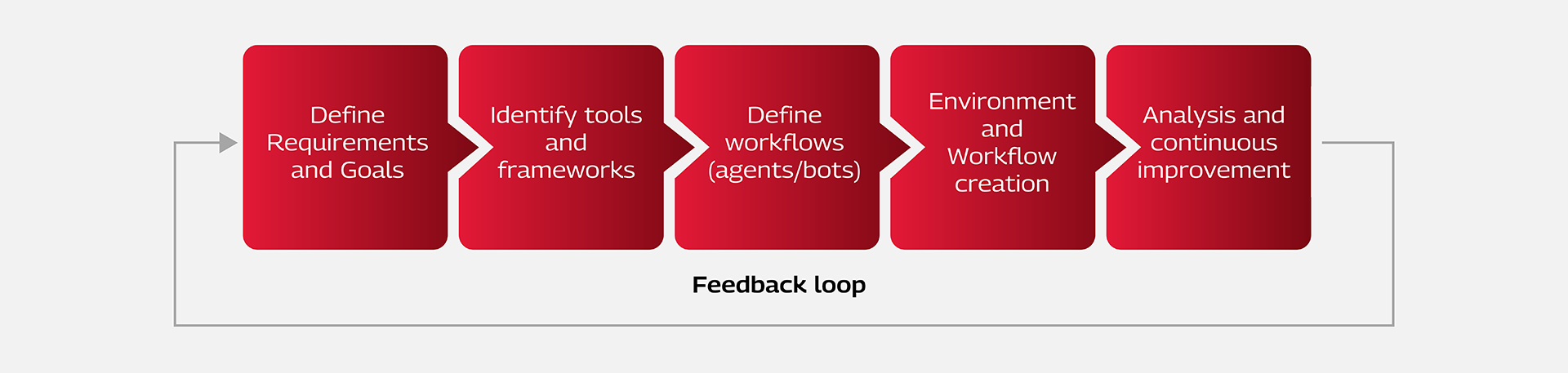
Below are a few Agentic AI use cases across the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). Each use case involves a specific set of steps that AI agents carry out to achieve the intended goal.
| SDLC Phase | Agentic AI Use Case |
|---|---|
| Requirements | Agentic AI can connect to ALM tools, refine user stories, and generate architectural designs based on project inputs |
| Development | Automates code creation, performs unit testing, and generates code documentation to accelerate development |
| Testing | The system creates test artifacts, including test data, to support thorough and automated quality validation |
| Deployment | Identifies suitable deployment strategies and integrates them with CI/CD pipelines for seamless delivery |
| Monitoring | Tracks application errors and health issues in real-time and takes corrective actions where needed |
| Improvement | The system enables self-learning by continuously updating itself and providing actionable feedback for future cycles |
Tech Mahindra’s Approach – Enabling Agentic AI with AppGinieZ
At Tech Mahindra, we’re actively building Agentic AI into our delivery models. Through TechM’s AppGinieZ, we are enabling intelligent, modular, and AI-powered software development that integrates seamlessly with engineering workflows. This is an advanced AI-powered solution designed to address a wide range of independent use cases across the software development life cycle. The solution leverages cutting-edge technologies, including large language models (LLMs), intelligent algorithms, and robust integration capabilities, to streamline and enhance development processes.
TechM AppGinieZ supports both Generative AI and Predictive AI use cases:
- Generative AI capabilities enable the automatic creation of code snippets, documentation, test cases, and numerous other assets. TechM AppGinieZ can generate outputs that accelerate development and reduce manual efforts by understanding user-defined and natural language prompts.
- Predictive AI features include intelligent forecasting, defect triage, and generating a requirement traceability matrix, as well as user journeys from server logs, enabling teams to address potential issues proactively.
As part of their innovation roadmap, ADMSNXT COE is actively working towards integrating Agentic AI capabilities into AppGinieZ. Agentic AI introduces autonomous, goal-driven agents that can plan, reason, and act on behalf of users.
Key Benefits of Agentic AI in Software Engineering
When implemented effectively, Agentic AI can deliver measurable improvements across the software development lifecycle:
- Efficiency gains of up to 60–70% by automating repetitive, low-value tasks such as documentation, code review, and test case generation
- Improved code quality and maintainability, driven by consistent agent-generated outputs and automated validations
- Reduced bug-fix effort, with studies showing up to 40% fewer manual interventions needed during release cycles
- Parallelized workflows, where multiple agents work simultaneously under a supervisor agent, reducing bottlenecks and manual coordination
These benefits translate into faster release velocity, lower development costs, and a greater focus on strategic tasks within the team.
Best Practices for Adopting Agentic AI
While the benefits are compelling, implementing Agentic AI at scale comes with its share of challenges. These include fragmented development environments, unclear role definitions for AI agents, a lack of automation frameworks, and the risk of over-reliance on autonomous outputs without proper validation.
To ensure successful implementation, organizations should follow a structured adoption path(implementation challenges):
- Define clear goals aligned with business outcomes and engineering metrics
- Select the right agent framework and tools to build modular, coordinated workflows
- Design trigger conditions and monitoring hooks to activate agents based on real-time system activity
- Integrate feedback loops for continuous learning and improvement, allowing agents to refine output over time
- Establish agent roles and responsibilities upfront, ensuring they’re seamlessly embedded across relevant SDLC phases
By starting small, identifying the correct use cases, and scaling based on measurable impact, enterprises can unlock the full potential of Agentic AI within their engineering ecosystems.
Moving from Automation to Autonomy
Agentic AI is poised to transform the workforce by introducing autonomous, intelligent agents that can assume multi-step responsibilities throughout the software lifecycle. This shift from prompt-driven output to goal-oriented orchestration marks the next phase of the adoption of enterprise AI. And it’s not theoretical because platforms like AppGinieZ are already enabling organizations to embed agent-led workflows, reduce manual effort, and accelerate delivery across engineering teams.
At Tech Mahindra, the future of software development lies in modular, AI-native systems that can adapt, scale, and improve with each cycle. Through our AppGinieZ framework, we’re helping enterprises move toward that future with one intelligent agent at a time.
Are you interested in exploring how Agentic AI can enhance the value of your engineering operations? Connect with our experts to learn more about AppGinieZ and Tech Mahindra’s approach to intelligent, autonomous SDLC automation.