Integration of Distributed Energy Resources (DER) to the Grid
De-carbonization & shifting to alternate energy sources is one of the business imperatives for utilities and it is presenting new challenges. One of the challenges is creation or modification of existing grid infrastructure to accommodate integration with DER grids.
The energy transmission & distribution system has evolved from large centralized power plants to smaller energy sources such as solar, comprising of large solar farms & roof mounted customer solar panels, & wind farms etc. Additionally, the DER landscape becomes complex due to need for large battery storage facilities. It is impacting the present grid operations as the adoption of DER is growing at a phenomenal rate and has different demands.
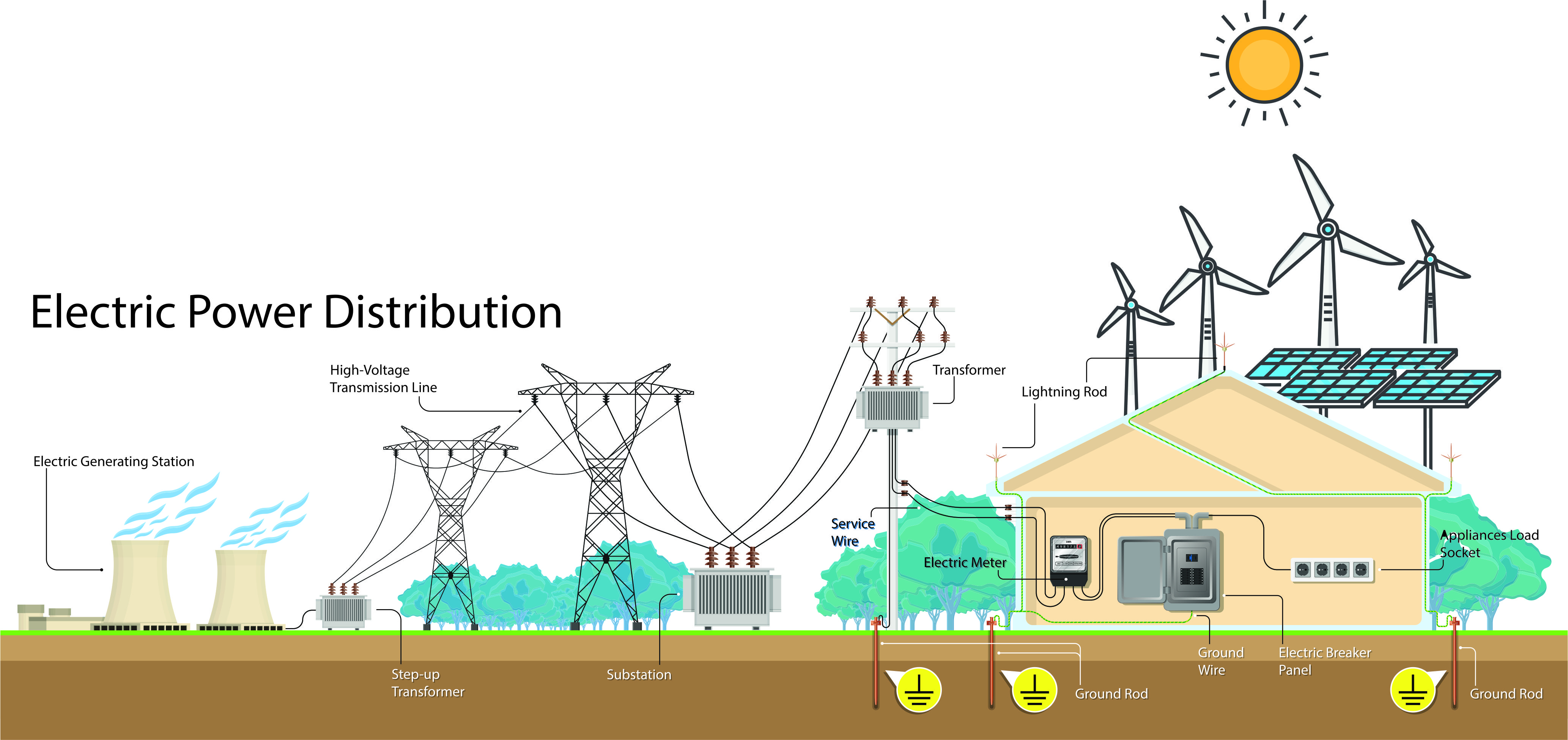
DER presents to the utilities a completely new business model. The traditional grid was not conceptualized & installed to address the DER related processes and the existing back end forecast engines & algorithms are not capable of accommodating these complexities. This becomes even more complicated for energy distribution companies that deal with dynamic demand & supply regularly.
The priority for the distribution companies is to work on the grid infrastructure to accommodate the DER related variations that may be not be easy to predict. Ensuring reliability & quality of supply to customer in this unpredictable demand supply chain is a challenge. Since the customers also play a pivotal role in the new eco-system, they need to have a better participation.
The revamped system will evolve out of the new business model that the DER brings about. It is still early days for the smart grid integration before it becomes a reality globally. Even the developed countries are deciding on the contours of the such systems and busy creating the infrastructure and the operating procedures around that.
Large investment is envisaged to bridge this gap and a careful assessment of costs & benefits is needed. Decision with respect to technologies to be used must be taken keeping local factors & long term goals in view.
The new system is expected to render energy efficiency through responsive demand & managing the solar & wind generation that is variable and is heavily dependent on natural factors

The collective value of the grid must ensure that the benefits accrue to new stakeholders including DER suppliers and customers.
In the design of new system and its SOPs the main components are as follows:
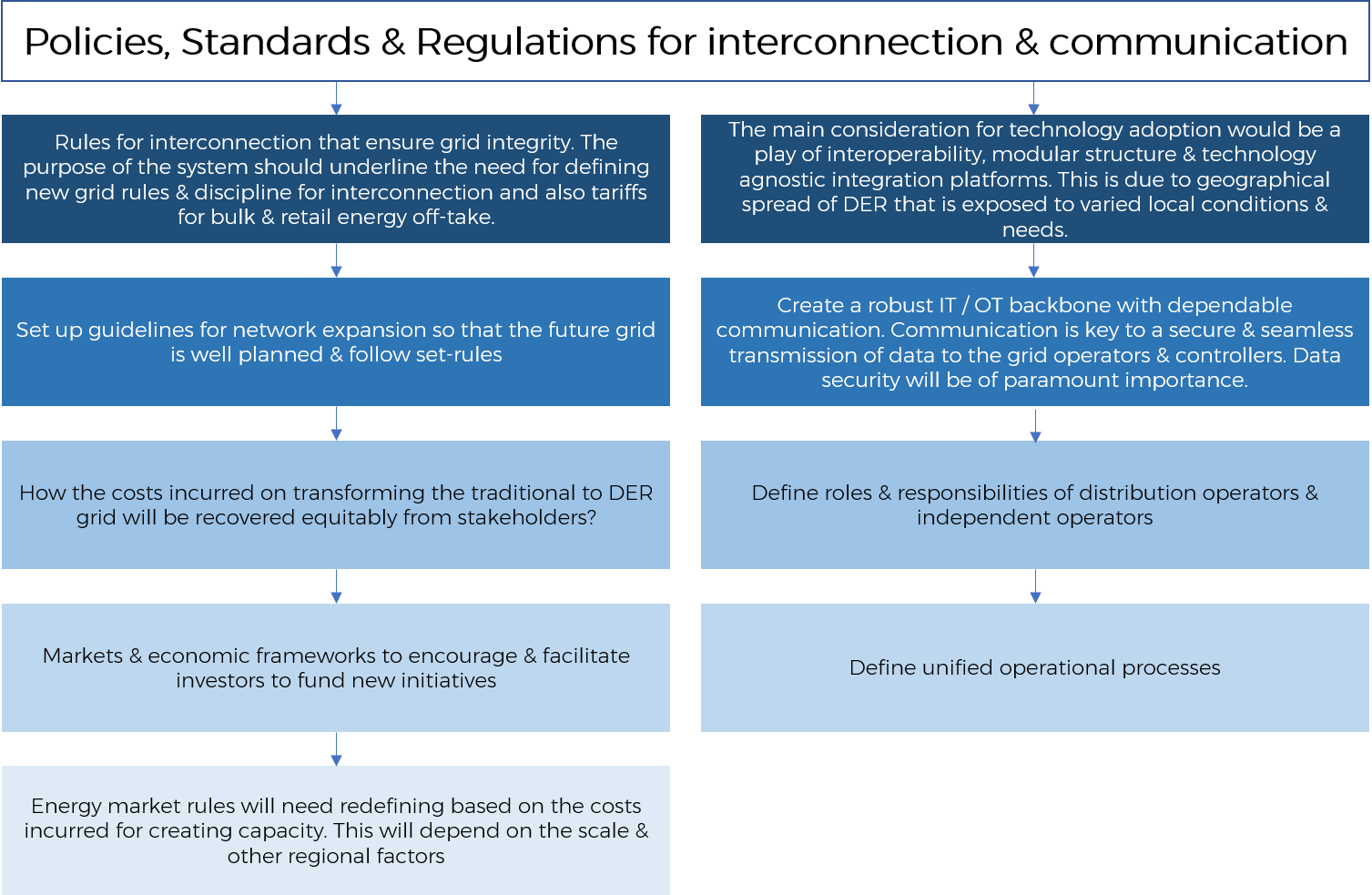
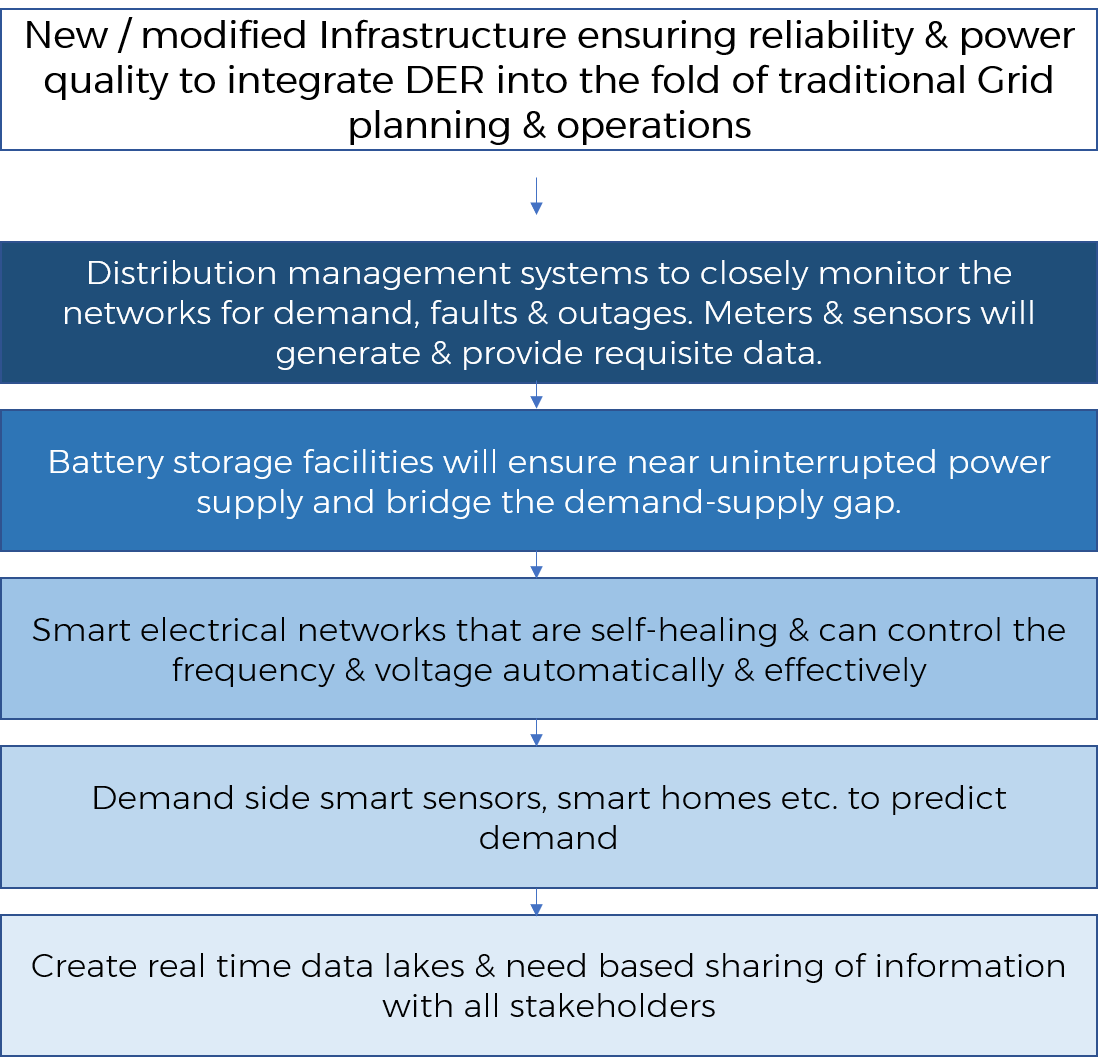
India Relevance
Grid Planning has traditionally been taking top down approach. But a radically different strategy may be relevant for a country like India.
In India the considerations for moving towards integrated grids will include not only financial & RoI related parameters but also social factors like subsidized power and rural demand & supply. Presently in rural electrification the last mile connectivity is a challenge. 100% electrification does not necessarily mean 100% household connected with power. In such a scenario an integrated grid, with rural household becoming a prosumer, will go a long way in creating the last mile connection & bringing power to each household.
Tech Mahindra Value
To summarize, maturing energy technologies, like solar generation, battery storage, and electric vehicles, are challenging the ways in which businesses engage with customers, giving rise to the “prosumer” acting as both micro supplier and consumer. In parallel, new, disruptive technologies ‒ particularly the Internet of Things and enterprise mobility ‒ are driving changes in consumer behavior, with smart devices enabling greater consumer control over energy consumption.
TechMahindra, as a technology service provider, has been actively supporting its utility customers for more than 15 years. For DER connectivity to the grid, there are multiple offerings that can be leveraged for connected utilities:
New technologies are presenting promising opportunities for improvements across the supply chain, including innovations in renewable energy resources.
To know more about Utilities offerings, visit our page here https://www.techmahindra.com/en-in/energy-utilities/










